Relativitätstheorie
Die Relativitätstheorie befasst sich mit der Struktur von Raum und Zeit, dem Verhalten von Masse in selbigen (SRT) und setzt das alles in Abhängigkeit zur Gravitation (ART).
Rückblick
Anfang des 20. Jahrhunderts fußte das naturwissenschaftliche Verständnis von Raum, Zeit und Gravitation noch auf der newtonschen Physik. Die newtonsche Physik malte uns ein Bild des Universums mit Raum und Zeit als absolute, d.h. unveränderliche und voneinander unabhängige Größen. Die Gravitation zeichnete er als Kraft zwischen zwei Massepunkten.
Überblick

In den Jahren von 1905 bis 1916 erfuhren diese Auffassungen dann eine radikale Revolution, ausgelöst durch eben jene Relativitätstheorie. Der theoretische Physiker Albert Einstein war maßgeblich an ihr beteiligt.
Die nächsten Abschnitte werden versuchen, die Grundlagen der Relativitätstheorie zusammenzufassen. Dabei muss der Prägnanz wegen auf Erläuterungen und Details verzichtet werden. Sie finden jedoch unter jedem Abschnitt Hinweise zu weiterführende Aufsätze. Falls Sie sich also näher für eines der aufregenden Phänomene der RT interessieren, klicken Sie sich einfach weiter.
1. Spezielle Relativitätstheorie
Häufig wird behauptet, Einstein habe Newton widerlegt. Das ist falsch, er verbesserte ihn lediglich durch eine allgemeinere Theorie. Mit seiner speziellen Relativitätstheorie entlarvte Albert Einstein nämlich Raum, Zeit und Bewegung als relative Größen. Die newtonsche Physik war damit entthront und ist in Einsteins Theorie nur noch als ein besonderer Grenzfall enthalten.
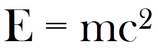
Doch nicht nur das, die spezielle Relativitätstheorie kann uns auch zeigen, dass Raum und Zeit gar nicht unabhängig voneinander existieren. Vielmehr verschmelzen die beiden in der SRT zu einer einheitlichen Raumzeit.
Auch die Masse M und die Energie E erwiesen sich in ihrer weltbekannten Gleichung (s.o.) als zwei Seiten derselben Medaille. Zusammengehalten werden diese schließlich noch durch die Lichtgeschwindigkeit C, die entgegen allen anderen relativen Bewegungen und Geschwindigkeiten immer konstant und unabhängig vom Bezugsystem ist.
2. Allgemeine Relativitätstheorie
Elf Jahre später entwarf Einstein seine Allgemeine Relativitätstheorie. Diese berücksichtigt auch die Fälle, in denen die Gravitation eine Rolle spielt. In zehn Feldgleichungen verwarf Einstein den newtonschen Gedanken, Gravitation sei eine Kraft, die sich ohne Zeitverlust ausbreite. Anstelle dessen fasst er die Gravitation als Eigenschaft der gekrümmten Raumzeit auf. Materie krümmt das Raumzeit-Kontinuum und so entsteht Schwerkraft.
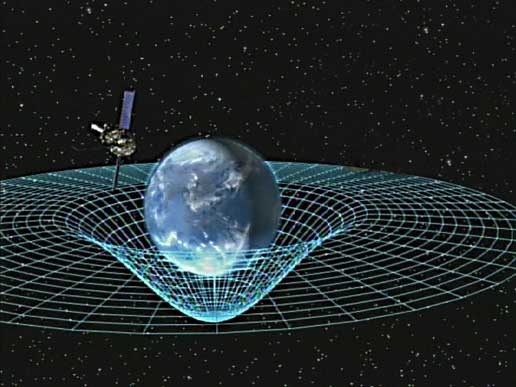
Das Schwerefeld kann man sich wie eine unsichtbare, gespannte Gummihaut vorstellen. Liegt nun ein massereicher Körper, etwa eine Sonne, in ihm, wird sie gekrümmt. Dementsprechend drückt sich auch die Gummihaut ein, wenn man einen Ball auf sie legt. Infolge der derart modifizierten Geometrie der Raumzeit ändert sich sogar der augenscheinlich so geradlinige Verlauf der Lichtstrahlen, die von den Massekörpern ausgehen. Erfasst vom Schwerefeld sucht sich der Lichtstrahl nun einen neuen, kürzstmöglichen Weg. Aus diesem Grund können wir auch noch die Sterne sehen, die sich eigentlich knapp hinter dem Sonnenrand verbergen.
3. Ausblick
Man kann sich wieder und wieder mit der Relativitätstheorie befassen und wird trotzdem niemals zu dem Gefühl kommen, alle ihre Konsequenzen durchgedacht zu haben. So geht es zumindest mir, immer wieder aufs Neue stehe ich vor Situationen, bei denen ich nicht weiß, wie man sie sich gemäß der RT denken soll. Oder die einem immer noch extrem komisch und unreal vorkommen.
Dabei lassen sich die Vorgänge und Eigenschaften innerhalb der Relativitätstheorie mathematisch unglaublich präzise beschreiben und gehören zu den bestbestätigten in der Geschichte der Naturwissenschaften. Dies klassifiziert sie, zusammen mit der Quantentheorie, als eine der besten Theorien der Gegenwart.
Zusammen mit der Quantentheorie stellt die Relativitätstheorie eine der zwei tragenden Säulen der modernen Physik dar. Beide gingen ursprünglich aus der newtonschen Physik hervor, enthalten diese immer noch als Spezialfall und erfüllen somit das Korrespondenzprinzip. Die Bemühungen vieler Physiker gelten dieser Tage der Vereinigung dieser beiden Säulen, wobei meist versucht wird die Relativitätstheorie in die Quantentheorie zu integrieren, und nicht andersrum.
In den Quantenfeldtheorien konnte man bereits die spezielle Relativitätstheorie mit der Quantentheorie und im Rahmen des heutigen Standardmodells der Physik einen. Der noch außenstehenden Quantentheorie, die auch noch die allgemeine Relativitätstheorie bzw. die Gravitation mit ins Boot nimmt, will man dann den Namen Quantengravitationstheorie geben.
4. Verweise
- Intelligenz: Albert Einstein war ein sehr intelligenter Mensch. Intelligenz aber ist kein reines Bücherwissen und nicht bloß das Resultat testorientiertem Spezialtrainings. Es ist vielmehr eine breite und tiefe Begabung zum Verständnis unbekannter Problemfelder.
- Raum und Zeit: Die Relativitätstheorie hat uns dem Wesen von Raum und Zeit erheblich näher gebracht. Sie kann aber nicht das letzte Wort gewesen sein, wie sich beispielsweise an Schwarze Löchern zeigen lässt.
- Sprache: Issac Newton meinte noch: “Die absolute, wahre und mathematische Zeit verfließt an sich und vermöge ihrer Natur gleichförmig, und ohne Beziehung auf irgendeinen äußeren Gegenstand.” Wir wissen es heute besser. Außerdem ist die Aussage „die absolute Zeit fließt gleichförmig“ tautologisch. Sie hat keinen Informationswert, da die absolute Zeit per definitonem immer gleichförmig fließt. Weil, wie könnte man den gleichmäßigen Fluss einer absoluten Zeit überprüfen, wen nicht mit der absoluten Zeit selbst und wie könnte uns ihr Fluss in diesem Fall anders erscheinen, als gleichmäßig? Ähnliches gelte für einen absoluten Raum, der beispielsweise nicht relativ ist. Was Raum und Zeit aber nach unserem heutigen Verständnis sei, geht vollkommen gegen das, was man intuitiv annehmen würde: Raum und Zeit sind keine Bühne, vor deren Hintergrund sich alles Materielle abspielt. Vielmehr sind Raum und Zeit intrinsische Eigenschaften der Materie, die ohne sie gar nicht existieren würde.
- Unser Problem: Was für die unanschauliche Quantenwelt gilt, gilt in abgeschwächter Form also auch für die Relativitätstheorie: Sie entspricht nicht unsere Alltagsmeinung und Intuition. Was sie aber nicht falsch macht. Wir erleben im Alltag nun mal so etwas wie die newtonsche Welt, sprich keine schnellen Bewegungen, keine kleine Skalen. Deshalb ist man auch lange Zeit so gut mit Newton gefahren. In weniger alltäglichen Situationen aber, wie etwa am Rande supermassiver schwarzer Löcher oder im Inneren eines Atoms, versagt Newtons Physik. Spätestens an dieser Stelle braucht es dann die Quantentheorie, und die Relativitätstheorie.
Stand: 2015
 Philoclopedia
Philoclopedia

Hiroji kurihara (Donnerstag, 28 November 2024 08:04)
Equivalence Principle
We can say that we can quantitatively grasp both gravity and inertial force. However, we cannot qualitatively grasp them. Do we have the right to claim equivalence principle ?
In fact, perhaps equivalence principle can be directly denied.
Hiroji kurihara (Freitag, 22 November 2024 01:49)
For free falling thought experiment,. pearl necklace would be bette than elevator. There will be other examples too. A real example is Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9, which fell on Jupiter in 1994.
Common theory of Mercury's perihelion shift is poor. Also, Newton's shell theorem should be reconsidered.
Hiroji kurihara (Montag, 18 November 2024 05:42)
Free Falling (Again)
Formula for gravity, G mM/r^2, and formula for inertial force, ma, are acting on pearl necklace. Gravity acts on each pearl with the magnitude indicated by the formula.
It is inevitable that gravity and inertial force cancel each other out totally (apparent) at a specific mass point.
Hiroji kurihara (Freitag, 15 November 2024 06:18)
Free Falling
Pearl necklace is falling freely in a vertical line. Gravity acting on each pearl is mM/r^2, and inertial force is ma. Mass of the string holding pearls is zero.
This post does not refer to equivalence principle.
Hiroji kurihara (Mittwoch, 13 November 2024 02:24)
Free Falling
On a celestial body below, two elevator cabins the same are falling freely. They are lined up one above the other and connected by a long string. Is some point on the string local inertial frame ?
Hiroji kurihara (Freitag, 01 November 2024 03:19)
Free falling
The two, gravity and inertial force can be expressed as force vectors. So, it is possible that the two cancel each other out in a free-falling elevator (as a phenomenon).
However, free falling is only one phase in which two vectors interact. There is no reason why free falling should be treated as something special.
Hiroji kurihara (Donnerstag, 31 Oktober 2024 03:58)
Equivalence Principle
A body of mass m is placed on flat surface (without friction). String pulls this body to the right with tension ma. The body accelerates to the right, and inertial force ma acts to the left. Magnitude of tension and inertial force are equal. This is as shown by Newton's third law of motion.
The fact that gravity and inertial force are equal (in total) in a free-falling elevator is probably due to Newton's third law of motion.
Hiroji kurihara (Dienstag, 29 Oktober 2024 04:33)
Free Falling
An elevator cabin is in free falling. Elevator is rigid body consisting of the same mass points with mass m. So, each mass point has the same acceleration. The same force acting on each mass point is ma.
There is no word equivalence principle in above explanation or any of the following. In fact, there should be no word equivalence principle.
Hiroji kurihara (Sonntag, 20 Oktober 2024 10:17)
Equivalence Principle (again)
Magnitude of gravity acting on a body (mass m) is GmM/r^2, and magnitude of inertial force is ma. For vectors of two forces, to cancel each other out is not prohibited (as phenomenon). In free-falling elevator, two forces cancel each other out (as phenomenon) in one local area totally and in other local areas partially.
As above formulas show, two forces are different. Real elevator do not support equivalence principle.
Hiroji kurihara it (Dienstag, 15 Oktober 2024 01:44)
Equivalence Principle
On state of being of vectors of gravity (attraction) and inertial force, there will be no restrictions. Therefore, vector of two forces will be possible to be compensate and nothing special happens. Like an elevator in free fall.
Force acting on us on surface of Earth is resultant force of gravity (attraction) and centrifugal force. On surface (solid or liquid) of planets of solar system, gravity (attraction), and centrifugal force (different planet’s rotation) is various. Equivalence principle is unacceptable.
Hiroji kurihara (Freitag, 11 Oktober 2024 01:15)
About Gravity
"Resultant force of attraction and centrifugal force of Earth is the true nature of gravity." This is cited from a website. However, I think that attraction in this citation is the true nature of gravity. This citation is evasive and delegate.
Equivalence principle is unacceptable. One reason is that, I can't recall ever seeing universal gravitational constant mentioned on inertial force.
Hiroji kurihara (Mittwoch, 09 Oktober 2024 10:11)
About Gravity
Following claims : Newton's spherical shell theorem, Perihelion shift of Mercury (claimed before relativity, before 1905) are unacceptable. My veiw are posted into some web-sites in English.
Also in relativity, I find no acceptable claim regarding gravity (equivalence principle is unacceptable). And I posted objections (that I can) to relativity's claims regarding gravity.
Hiroji kurihara (Freitag, 04 Oktober 2024 01:28)
Centrifugal Force is not Fictitious
Centrifugal force that is accompanied by rotational motion is inertial force, that is, real force, action. Reaction to it is a centripetal force (In case of hammer throwing wire, it can also be tension, tensile stress). Its reality and magnitude is one and only. From any frame.
The same is true for all curvilinear motion.
Hiroji kurihara (Donnerstag, 03 Oktober 2024 06:57)
Centrifugal Force is not Fictitious (again)
On a plane, two rods cross each other (without friction) and rotate around intersection point. This basic form can be transformed as follows.
1) Body of mass m is attached to both ends of one rod. Body of mass 2m is attached to both ends of the other rod. Mass of rods is assumed to be zero.
2) Body of mass m is attached to each of four ends of two rods. Length of one rod is a, and length of the other is 2a. Mass of rods is assumed to be zero.
.
Centrifugal force and tension acting on rods are real forces, not fictitious. From any frame.
Hiroji kurihara (Samstag, 07 September 2024 04:34)
Inertial Force is not Fictitious (Summary)
Spaceship is moving horizontally with uniform acceleration. Body m is pushing against rear wall of the spaceship's cabin (A). Rear wall pushes back the body with normal force (B). A is action, B is reaction.
Spaceship is moving horizontally with uniform acceleration. String attached to front wall of the spaceship's cabin stretches backward inside the cabin, pulling body m attached to rear end of string (A). The body resists pulling force of string (inertial resistance) (B). A is action, B is reaction.
To begin with, distinction between action and reaction seems to be unclear.,11
Hiroji kurihara (Freitag, 06 September 2024 07:37)
Acceleration and Non-Acceleration (again)
Imagine a human being in accelerating passenger car and a station staff standing on platform. Now, it is a thought experiment. What if increasing acceleration g is at the level of an unmanned missile ?
Difference between acceleration and non-acceleration is not fictitious. The two are physically different. Again, because it is big problem.
Hiroji kurihara (Dienstag, 03 September 2024 10:39)
Acceleration and Non-Acceleration
A spherical fluid is floating in space. The fluid is uniform and isotropic. That is, gravity has no acting on the sphere.
The sphere will be in non-accelerated frame. It is moving in a uniform linear motion through space (or is at rest). However, if the sphere moves in a way other than the above, there will be a corresponding deviation from uniform isotropy. Difference between accelerated and non-accelerated frame will not be fictitious.
Hiroji kurihara (Montag, 02 September 2024 09:44)
Acceleration and Non-Acceleration
A body is being pulled by strings from the left and right. Tension in the strings is the same, ma. The same body is being pulled by one string from the left and by two strings from the right. Tension in all three strings is the same, ma. Let the body in two figures be A and B.
Are A seen from B and B seen from A symmetrical ? No, that's not, because the internal stresses in body A and B are different.
Hiroji kurihara (Donnerstag, 29 August 2024 02:15)
Inertial force is not Fictitious (rewritten)
A spaceship is moving horizontally with uniform acceleration. Inside the spaceship, a body m is pushing against the rear wall. This force is action, and is inertial force. As reaction, and as normal force, the rear wall pushes back against the body. Magnitude of the two is ma.
Above explanation should be valid for one inside and outside the spaceship. Inertial force will be a real force for everyone, and will not be fictitious.
Hiroji kurihara (Samstag, 24 August 2024 05:13)
Sorry, not a latest test was posted. Allow me to post again.
Accelerating Frame and Non-Accelerating Frame (fragmentary)
◎ An observer in a passenger car in uniformly accelerating linear motion will see everything in the car as at rest ? What if g is large ?
◎ A website says that equiliblium of forces are only for frames that are at rest or in uniform linear motion.
◎ The difference between accelerating frame and non-accelerating frame is crucial. But we continue to turn away from to it. This is physics ?
◎ A string stretches horizontally inside the cabin of a spaceship moving to the right with a uniform acceleration. The right end of the string is fixed to the right inner wall of the cabin, and the left end is fixed to body m, which is floating inside the cabin. The string has a tension ma (ignore the mass of string). Both m and a are specific values.
Note) m and a will be the same for one inside and outside the ship.
Hiroji kurihara (Samstag, 24 August 2024 04:31)
Accelerating Frame and Non-Accelerating frame (fragmentary)
◎ An observer in a passenger car accelerating at a uniform speed will see everything in the car as at rest. What if g is large ?
◎ A website says that equiliblium of forces are only for framess that are at rest or in uniform linear motion.
◎ The difference between accelerating frame and non-accelerating frame is crucial. But we continue to turn away from to it. This is physics.
◎ A string stretches horizontally inside the cabin of a spaceship moving to the right with a uniform acceleration. The right end of the string is fixed to the right inner wall of the cabin, and the left end is fixed to body m, which is floating inside the cabin. The string has a tension ma (ignore the mass of string). Both m and a are specific values.
Note) m and a will be the same for one inside and outside the ship.
Hiroji kurihara (Dienstag, 20 August 2024 06:03)
Inertial Force is not Fictitious (rewritten)
Inertial force of a body moving in uniformly accelerated linear motion is based on m and a. There can be no denying. In addition, ma = F. In short, inertial force is not fictitious.
Hiroji kurihara (Sonntag, 18 August 2024 07:22)
Inertial Force is not Fictitious
In actual examples of action and reaction in Newton's third law of motion, sometimes, it is unclear which is action and which is reaction. But it must be clear that inertial force can be either of the two. Then inertial force must be real force. For everyone.
In the well-known formula F = ma, which is inertial force ? It can be ma. Then inertial force must be real force. For everyone.
Hiroji kurihara (Donnerstag, 15 August 2024 04:40)
Inertial Force is not Fictitious (rewritten)
Inside the cabin of a spaceship moving with uniform acceleration to the right, a string stretches. Right end of the string is tied to the right inner wall of the cabin, and left end is tied to a body m, floating inside the cabin. There is tension ma in the string (ignore mass of the string).
This physical fact and its explanation must be the same for one inside and outside the spaceship.
Hiroji kurihara (Montag, 12 August 2024 00:23)
Compound Nouns
Gravitational acceleration, local inertial frame, inertial mass, gravitational mass. Only four compound nouns. Sorry for my shallowness. But, probably or clearly, these four will be forcible.
Hiroji kurihara (Mittwoch, 07 August 2024 03:19)
Statics or Dynamics ?
A point (point of action) is pulled left and right by strings with a vector F, creating balance. Next, can the force on the right be considered an inertial force ? At right end of the right string, a body with mass m is placed. In other words, tension ma is acting on the right string. In this pictere, the whole is moving to the left with a uniform acceleration.
Note: This is a horizontal free falling.
Hiroji kurihara (Samstag, 03 August 2024)
Inertial Force is not Fictitious (rewritten)
An body m is suspended by a string from the center of the ceiling of a passenger car. If passenger car is accelerated to the right, string and body will tilt downward to the left. But, what if passenger car is jerk-moving? The inclination of string and body will continue to increase, the tension in string will increase, and eventually the string will break.
These situations and explanations of the situation must be the same for one inside and outside passenger car. Inertial force is not a fictitious force for one inside and outside the car. Inertial force in this case is action, and the reaction is the tension in string.
Hiroji kurihara (Samstag, 20 Juli 2024 00:43)
Inertial Force is not Fictitious (rewritten)
By a string, a body of mass m is hanging from the ceiling in the center of the passenger car. Body and the string are perpendicular. Next, the passenger car begins to accelerate to the right. Body and the string tilt to the left. This acceleration is usually constant. However, if an external force F continues to grow as time passes, the inclination of body and the string also continues to grow.
These pictures will be the same for one inside and outside the passenger car. And, the tension of the string which is reaction to the inertial force will be the same for the two also (and if the string breaks, it will be the same for the two also).
Hiroji kurihara (Dienstag, 09 Juli 2024 03:17)
Speed of Starlight (Supplement)
Allow me to add to latest posts. When the glass cube moves left and right….
Inside the glass, c/n is constant, and the other two are variable
Just before entering the glass, λ is constant, and the other two are variable
Just after leaving the glass, c is constant, and the other two are variable
Hiroji kurihara (Samstag, 15 Juni 2024 06:20)
Speed of Starlight
Sorry, in the first line of formula, letter "j" was added. Please read it as follows.
Difference inside the glass c/n = c/n f ≠ f λ ≠ λ
Hiroji kurihara (Samstag, 15 Juni 2024 03:31)
Speed of Starlight
A glass cube is floating horizontally in outer space. Two rays of starlight coming from the left and right are passing through the glass horizontally. Below is the difference between the two rays of light as seen from viewpoint of the glass (difference in formula v = f λ).
Difference inside the glass cj/n = c/n f ≠ f λ ≠ λ
Difference just before entering the glass c ≠ c f ≠ f λ = λ
Difference just after leaving the glass c = c f ≠ f λ ≠ λ
Hiroji kurihara (Donnerstag, 13 Juni 2024 04:45)
Measuring λ of Starlight
How is λ of starlight measured ? One thing is certain. The λ before it enters measuring device is not be varied with the motion of measuring device. So, if measuring device is moved, it will become clear which λ was measured (which λ of starlight before extinction or after extinction).
Hiroji kurihara (Sonntag, 09 Juni 2024 08:37)
Allow me to revise the first “Note” of my post (most recent). Sorry.
Note) For light before it reaches the glass, formula v = f λ also holds (from perspective of the glass). And value f is the same as f for the glass.
Hiroji kurihara (Freitag, 07 Juni 2024 23:53)
Value of Speed of Light (of starlight in outer space)
Light of two stars coming from the left and right is passing through a glass cube. This cube is floating horizontally in outer space. Inside the glass, formula c/n = f λ holds on starlight. Four values are known.
Two lights inside the glass are spectralized and the spectrum (distance between chosen atom or molecule A and B) is compared. The distance will be slightly different.
Note) For light in outer space, formula v = f λ holds. And value f is the same as f for the glass (from perspective of the glass).
Note) It seems that extinction does not conceal the difference of spectrum.
Hiroji kurihara (Mittwoch, 05 Juni 2024 04:15)
Speed of Light is not Constant Always (again)
From the left, a starlight is coming to a glass cube floating in outer space, and is leaving to the right. At the left and right end of the glass each, frequency of starlight is the same. Imagine that the glass is moving at various uniform speeds to the left and right. Then, v of light on the left and right will not be the same, and so will λ (the formula v = fλ is viewed from perspective of the glass).
Hiroji kurihara (Sonntag, 02 Juni 2024 01:14)
Extinction
Light entering glass from outer space has a speed of c/n relative to the glass. This equalisation in speed within the medium is called extinction, and is completed in a very small optical path length that differs depending on mediums. For glass, it is 0.0001 mm.
Imagine that the glass moves in various uniform linear motions in outer space. The speed of light entering the glass and leaving the glass are not the same (from the perspective of the glass).
Hiroji kurihara (Dienstag, 28 Mai 2024 02:07)
Wavelength Measurement (supplement)
A starlight is passing through horizontal tube in outer space from left to right. A flat glass plate is fitted in center of the tube. Imagine that this tube is moving at different uniform speed in left and right directions. For left and right light each, the formula v = f λ holds. Frome the perspective of the tube, f on the left and right sides are the same. But v will be different and λ will also be different.
There is an argument that v are the same. If so, λ must also be the same. However, λ on the left does not follow (does not be affected by) the motion of the tube. But λ on the right follows (is affected by). This difference must not be forgotten.
The wavelength of light and the speed of light each is not the same before and after extinction.
Note) For glass, extinction is done in the distance of 0.0002 mm.
Hiroji kurihara (Freitag, 24 Mai 2024 09:03)
Wavelength Measurement (Aw)
Is wavelength of light traveling in outer space being measured as it is (on light before arriving) ? Isn't what is being measured light (extincted light) that has passed through a medium such as glass ? In internet (a bit), any site mentioned can not be found.
Suppose an observer moving in various motions in outer space is measuring wavelength of starlights. In the formula, c = f λ, f varies. Accordingly, c varies. However, we seem to believe, it is λ that varies.
We must distinguish the light before and after measurement device (before and after extinction).
Hiroji kurihara (Mittwoch, 22 Mai 2024 05:18)
Hollow Tube and Speed of Light (again)
In outer space, starlight coming from the left is passing through a stationary horizontal tube of length L. Frequency at the left and right ends of the tube is the same. This sameness is true even if the tube is moving in the left and right directions at different uniform speed. In other words, number of waves that exist inside the tube (wave number × L) is invariable. There is no varying in wavelength of light. In the formula, c = f λ, it is f and c that vary. It is the first picture.
In the second picture, there are two tubes the same as above. The two are moving at a uniform speed. One is to the left and the other is to the right. As mentioned above, wavelength of light is the same. In the formula, c = f λ, f and c (of the two) are not the same.
Hiroji kurihara (Sonntag, 19 Mai 2024 12:28)
From today's post, erase the word "Aether" (fourth word in text), please. Sorry.
Hiroji kurihara (Sonntag, 19 Mai 2024 11:45)
Aether Drift (again)
Speed of lightAether is the distance that light travels in one second, 299,792,458 m/s (defined value). Above value was obtained by measuring frequency and wavelength of laser light performed by Evenson et al in 1973 (error was ± 1.2 m/s).
Imagine frequency and wavelength of light coming from two fixed stars located at symmetrical points (at opposite ponts) on the celestial sphere. Measuring must be done simultaneously. Perhaps many of the measured speeds of light are different. If so, it will be possible to identify two points (on the celestial sphere) where the difference is greatest.
Note) Differences due to known mtion of Earth such as revolution and rotation must be excluded.
Note) Wavelength must be measured before the light enters mediums such as glass. Is it possible ?
Hiroji kurihara (Samstag, 18 Mai 2024 10:08)
One-way Speed of Light/Isotropy of Aether (again)
English version of Wikipedia has an item titled "One-way speed of light". Word isotropic is found in 27 places.
However, if the light from multiple celestial bodies on the celestial sphere is recorded and analyzed in outer space, one-way speed of light will become disclosed. Probably easily. By established means of measuring aberration.
The position of bright lines and dark lines in spectrum of the celestial body's light will show the speed of celestial body's light and speed of light relative to Earth (and Aether drift). The isotropy and uniformity of aether will also be disclosed
Hiroji kurihara (Sonntag, 12 Mai 2024 07:36)
Lunar Laser Ranging (again)
Distance between Moon and Earth is measured with millimeter precision. Measurement is based on the formula “distance = speed of light x round trip time / 2”. What is noteworthy here is that the direction of laser beam with respect to celestial sphere does not affect the measurement results.
Assume that the space where Moon and Earth exist is also filled with aether. Measurement results will differ depending on the direction of laser beam with respect to celestial sphere (according to the explanation of MM experiment).
However, aether does not affect the propagation of electromagnetic waves at the distance between Moon and Earth. That is, aether does not affect the propagation of electromagnetic waves for a few seconds after emission. Ritz’s emission theory is revived, although in a limited extent. For now, let’s take this as an assumption. There is no need to be worried about the framework of time or space.
Hiroji kurihara of (Samstag, 04 Mai 2024 02:53)
Law of Universal Gravitation (rewritten)
Formula for the law of universal gravitation is F=GMm/r^2. Value r is the distance between centers of gravity of the two bodies (let’s call them spheres L and R). If r is 50, the squared is 2500. It is the first diagram.
Now, this is the second diagram. On a horizontal straight line, spheres L, R1, and R2 are lined up. If distance between L and R1 is 49, and distance between L and R2 is 51, the squared are 2401 and 2601. If these two are added and divided by 2, the value 2501 is gotten, which is slightly larger than 2500. In other words, the formula of universal gravitation doesn’t care about the size of the two sources of gravity, but in reality, there will be some effect, even if it’s a little ? Is Newton’s spherical shell theorem not perfect ? Is this the main cause of apsidal precession ?
Note) 2500 and 2501 are coefficients in numerator of the formula.
Note) Masses of R1 and R2 each are 1/2 of the mass of R.
Note) Assume that R1 and R2 are hemispheres of R (distance of centers of gravity is 2).
Hiroji kurihara (Samstag, 27 April 2024 07:13)
Accelerated Motion and Non-Accelerated Motion (again)
All accelerated motion is accompanied by inertial force (it is reaction. See Newton’s third law of motion).
All non-accelerated motion is not accompanied by inertial force. It is the same for absolute rest (relative to aether frame).
Gravity is unrelated to this problem.
Hiroji kurihara (Samstag, 20 April 2024 03:48)
Equivalence Principle (again)
Allow me to repeat the previous question,regarding two situations ◎ below. Two situations ◎ can be explainend qualitatively and quantitatively using formulas based on Newton’s laws of motion. The question is, how to explain equivalent principle ? Is there anyone who can ? .
◎ Forces of the same magnitude are acting on a mass point from the left and right directions. Types of forces are tension, gravity, and inertial force. Since there are no combinations of inertial forces and inertial forces, there are five combinations of forces (ignoring the difference between left and right).
◎ A body is sliding down inclined surface (no friction).
Hiroji kurihara (Freitag, 19 April 2024 06:04)
Equivalence Principle (again)
On the ground, a passenger car is moving with uniform acceleration to the right. In the car, a body hanging from the ceiling with a string is swinging to the left. The angle can be explained qualitatively and quantitatively using equations based on Newton’s laws of motion. What about equivalence principle ? Is there anyone who can ?
Hiroji kurihara (Dienstag, 16 April 2024 10:16)
Accelerated Motion and Non-Accelerated Motion (again)
Difference between the two motions above will be the difference of motion with respect to aether frame. A mass point moving in accelerated motion is accompanied by inertial force, that corresponds qualitatively and quantitatively. A mass point moving in non-accelerated motion (uniform linear motion) is not accompanied by inertial force.
A saying are trying about inertial force and gravity. What can we say by comparing the two words ? Inertial force is inertial force, gravity is gravity and both are true forces ! That seems to be all that can be said. This is a short report.
Hiroji kurihara (Freitag, 12 April 2024 10:11)
Local Inertial Frame (again)
An elevator cabin is in free fall. Imagine mass points placed regularly in the elevator. Vector of inertial force acting on each mass point is the same. Local inertial frame is impossible.
Two elevators are moving apart horizontally. One is in accelerated motion and the other is in non-accelerated motion. By an accelerometer, to tell which one is accelerating is possible. In the elevator with accelerated motion, there is no inertial frame, even locally. this
Hiroji kurihara of (Freitag, 12 April 2024 09:01)
Accelerated Motion (again)
A passenger car is accelerating to the right (uniform acceleration). A light source (wavelength is onstant) at the rear wall of the car emits light, and on the front wall, frequency measuring device is settled. During acceleration, in the car, there will be more waves than before. In other words, accelerated motion is not fictitious (inertial force will not be fictitious also).
A ray of light is emitted from the ceiling of a passenger car directly below. When this car is accelerated, the light ray reaches the floor in a parabola. Difference between acceleration and non-acceleration is not fictitious.